- Services
- Metals (overview)
- Plastics (overview)
- CAD Design
- Rapid Prototyping
& Rapid Tooling - CNC Machining
- Finishing & Assembly
- Rubber Plaster Molding
- Precision Airset Sand Casting
- Graphite Mold Die Casting
- One-Shot Casting
- Reaction Injection Molding (RIM)
- Rapid Injection Molding
- Design for Manufacturability (DFM)
Technical Information: Graphite Die Casting for Metal Components
How, When & Why to Use It:
- To produce precision and premium quality aluminum and zinc castings with the exact properties of die castings.
- For aesthetic applications where appearance is critical.
- Prototyping - to assist engineering in debugging design before committing to hard tooling.
- For low volume applications where quantities do not justify production die cast tooling.
- For castings with thin walls or where weight is critical.
- To functionally test die castings prior to investing in hard tooling.
- Tooling is low cost and allows ease of modification.
- To reduce "time to market" on new programs and evaluate market potential.
- To reduce time for machining and secondary operations.
- To fill the gap if dies are lost, damaged or delayed.
- To assist and reduce time for U.L. approval.
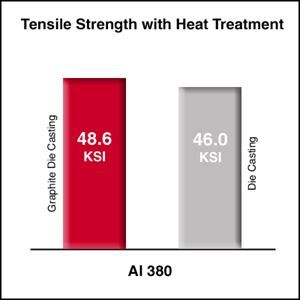

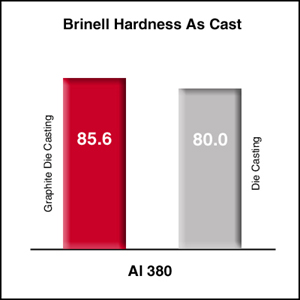
Design & Technical Information
Size
Less than 14 x 14 x 14 inches.
Finish
63 micro-inch.
Wall thickness
>0.100 inch.
General tolerances
+/- 0.005 inch plus 0.0015 in./inch
Alloys
Aluminum and zinc alloys common to die casting.
- Aluminum: 356, 380 and 390
- Zinc (Zamac): ZA-3, ZA-8, ZA-12
Draft
Same as die cast parts.
Cost
Rule of thumb for complex shapes within a 14 in. cube:
Tooling: 25-30% of die cast tools.
Piece price: 5 times die casting price.
Delivery
3 - 5 weeks for tooling
30 to 100 pieces cast per day




